Introduction
In the industrial goods and machinery sector, spare parts availability is mission-critical. From turbines and compressors to mining trucks and CNC machines, downtime due to missing or delayed parts can stall entire operations. Traditionally, OEMs relied on massive spare parts warehouses, stocking thousands of components globally. While this ensured availability, it locked up hundreds of millions of dollars in working capital and still failed to guarantee timely delivery.
The global spare parts market is worth more than $400 billion annually, yet inefficiencies persist. Warehouses overflow with slow-moving inventory, while customers wait weeks for niche parts. At the same time, sustainability concerns have made global supply chains less acceptable. Companies are now pressured to find leaner, greener, and faster solutions.
This case study examines how a leading European industrial machinery supplier embraced 3D printing and digital twin technology to reimagine its spare parts supply chain—reducing costs, accelerating delivery, and slashing emissions.
The Challenge
The client, serving customers across construction, mining, and power generation, faced severe pain points:
-
Excessive Inventory Costs: Over $500 million was tied up in warehouses worldwide, much of it slow-moving or obsolete.
-
Long Lead Times: Customers often waited 6–8 weeks for rare spare parts, jeopardizing project timelines.
-
Obsolete Components: Machines in the field for 15–20 years required parts that suppliers had stopped producing. Customers often resorted to grey-market parts, raising quality and safety risks.
-
High Environmental Footprint: Shipping spare parts globally led to high CO₂ emissions, contradicting the company’s sustainability commitments.
The client recognized that traditional models—warehousing, bulk production, and long-distance shipping—were outdated in the Industry 4.0 era.
The Solution: Spare Parts 4.0 Strategy
The consulting team devised a bold plan leveraging 3D printing (Additive Manufacturing) + Digital Twins to create a distributed, on-demand supply chain.
Phase 1: Digital Twin Creation
-
Engineers scanned and modeled 20,000+ spare parts into digital blueprints using CAD and 3D scanning.
-
Each part was stored in a secure cloud-based library, accessible by regional service centers.
-
Advanced metadata tagging ensured traceability, compliance, and material standards.
Phase 2: 3D Printing Hubs
-
Deployed additive manufacturing hubs in strategic regions (Europe, Asia, North America).
-
Machines capable of printing in metals, polymers, and composites were installed.
-
Collaborated with local certified partners to scale printing capacity.
Phase 3: AI-Powered Demand Forecasting
-
Machine learning algorithms analyzed historical data and IoT signals from customer machinery to predict spare parts demand.
-
Predictive analytics prioritized which parts should be printed in advance versus on-demand.
Phase 4: Circular Economy Integration
-
Used recycled metals and polymers to 3D print parts, reducing material waste.
-
Customers could also send worn-out parts for remanufacturing, extending product lifecycles.
Results Achieved
Within 18 months, the transformation delivered dramatic improvements:
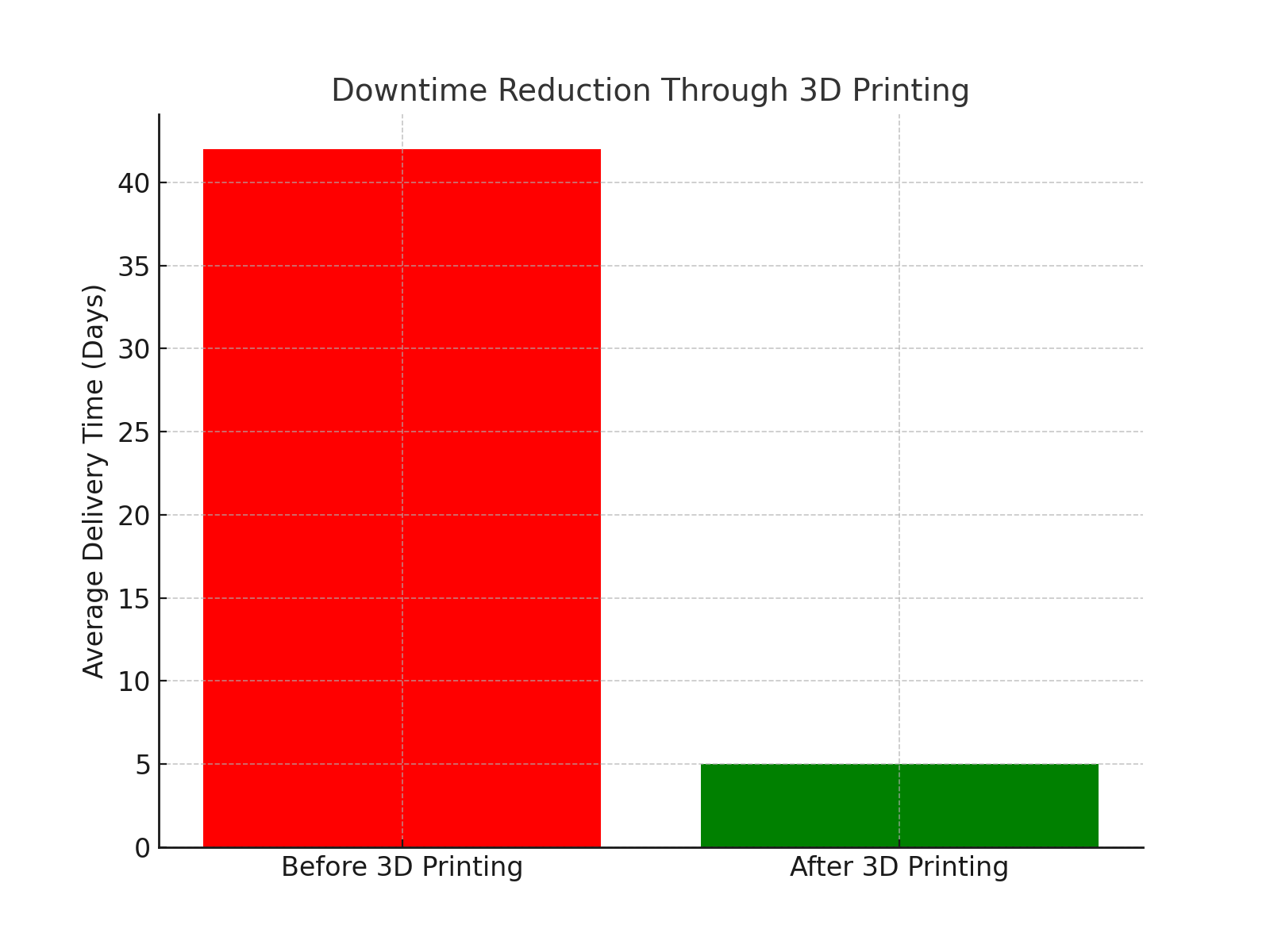
-
70% Reduction in Inventory Holding Costs: $350 million freed up in working capital by slashing physical stock.
-
80% Faster Spare Parts Delivery: Lead times dropped from 6–8 weeks to 3–5 days.
-
90% Resolution of Obsolescence Issues: Digital twins enabled the on-demand production of discontinued parts.
-
20% Lower CO₂ Emissions: Localized production cut shipping needs drastically.
-
Customer Satisfaction Boost: Clients reported higher equipment uptime and reduced reliance on unauthorized suppliers.
Competitive Benchmarking
-
Traditional Warehousing Model: High CAPEX, long lead times, inflexible.
-
Hybrid Stock + Local Production: Lower costs, but limited scalability.
-
Digital Twin + 3D Printing Model: Minimal inventory, maximum flexibility, and ESG-compliant.
The client became an industry pioneer, gaining first-mover advantage in spare parts digitalization.
Challenges Faced During Implementation
-
Certification & Quality Assurance: Parts for safety-critical machinery required rigorous validation.
-
Material Consistency: 3D printing materials had to meet strict durability standards.
-
Change Management: Customers and internal staff needed training to trust on-demand printed parts.
These hurdles were addressed through pilot programs, global certification partnerships, and awareness campaigns.
Strategic Insights
-
Digital Twins Unlock Scalability: Once parts are digitized, they can be printed anywhere, anytime.
-
Customer Loyalty Through Availability: Solving obsolescence and long lead times dramatically improves trust.
-
Sustainability Advantage: ESG-conscious clients prefer suppliers who lower environmental footprints.
-
The Future is Distributed Manufacturing: Decentralized, local production hubs will reshape global industrial supply chains.
Future Outlook
-
Integration of AI-driven generative design to optimize spare parts beyond original specifications.
-
Use of blockchain for part authenticity verification.
-
Expansion to field-based mobile 3D printers, allowing on-site spare part production in remote mining and energy sites.