Executive Summary
Helicopter services occupy a niche but strategic layer of global aviation: short-range vertical mobility that supports energy, emergency services, law enforcement, off-shore logistics, and specialized aerial work. In an era defined by urbanization, climate imperatives, and geopolitical shifts, helicopter services encompassing emergency medical evacuation (EMS), offshore energy support, tourism, and emerging urban air mobility (UAM), offer unparalleled agility.
Post-pandemic demand recovery, fleet modernization, and emerging vertical mobility technologies are reshaping service offerings and cost structures. With global civil helicopter fleets exceeding 30,000 units and annual deliveries surpassing 800 aircraft, stakeholders must prioritize strategic investments in sustainability and digital integration to capture enduring value. Over the next decade, operators who pair disciplined asset management, digital operations, and targeted service bundles (HEMS, offshore, aerial work, corporate/VIP) will capture premium margins while reducing operational risk.
Market Overview: Resilience Amid Volatility
The global helicopter services ecosystem demonstrates robust operational scale, underpinned by steady fleet growth and diversified applications. As of 2024, the turbine-powered civil helicopter fleet alone comprises over 21,000 units, led by Airbus Helicopters (~9,480 aircraft), Bell (~7,655), and Leonardo (~2,265). Including piston models, such as Robinson’s dominant 8,050-unit portfolio, the total civil fleet approaches nearly 35,000, a 32% increase from the year 2020.
Deliveries underscore this momentum: Airbus reported 346 units in 2023, rising to 361 in 2024, while Leonardo achieved 185 in 2023, reflecting a 24% year-over-year surge. The value of these shipments are estimated at over $5 billion for 2023, a 10.5% uplift, signaling sustained demand across commercial and parapublic sectors. Operationally, rotary-wing activity supports critical missions where in U.S. only air medical transport (AMT) accounts for over 0.5 million flight hours annually.
Safety metrics reinforce market maturity. EASA’s 2023 Annual Safety Review documents 10 fatal helicopter accidents across all European operations in 2022, yielding 24 fatalities, a figure aligned with the decade’s median of 24, despite a 10% rise in exposure. Globally, ICAO’s emphasis on rotary-wing risk mitigation, including enhanced GNSS resilience, has curbed accident rates to below 2 per 100,000 flight hours in mature regions. These indicators affirm helicopter services as a low-risk, high-reliability domain, essential for just-in-time logistics in remote or congested environments.
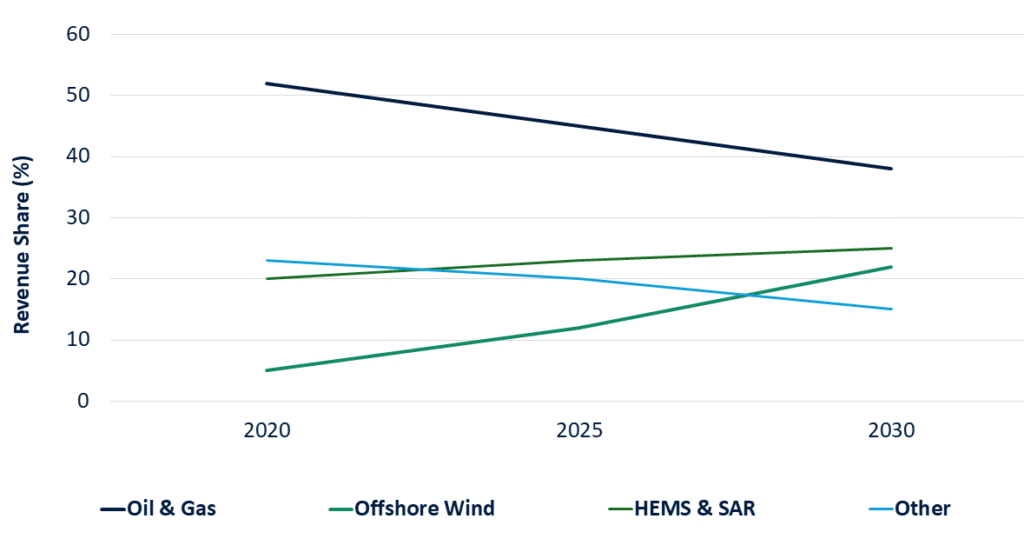
The Shifting Core of Helicopter Services: Projected Revenue Shift from Traditional Oil & Gas to Emerging Sectors
Regional Perspectives: Tailored Strategies for Divergent Landscapes
Geographic variances demand bespoke approaches. North America dominates with 33% of the global civil fleet, fueled by commercial helicopters supporting EMS and oilfield operations. U.S. operations logged millions of flight hours, with AMT alone averaging nearly 1,500 of daily flights. Operators should leverage FAA’s UAM Concept of Operations (ConOps) to integrate vertiports, potentially unlocking $1 trillion in economic value by 2040 through reduced ground congestion.
Europe, holding over 25% of the fleet, emphasizes regulated growth. The region’s focus on single-pilot IFR enhancements aligns with ICAO’s Global Aviation Safety Plan, targeting a 50% risk reduction. For operators, this translates to opportunities in cross-border EMS networks, bolstered by Eurocontrol’s airspace harmonization.
Asia-Pacific, with over 4,200 civil turbine helicopters, emerges as the growth epicenter. Multi-mission applications (~55% of fleet) drive demand in offshore and SAR. China’s CAAC approvals for eVTOL prototypes signal UAM acceleration, mirroring NASA’s performance modeling for low-noise urban ops. Investment in projects like Singapore’s vertiport hubs to secure seamless helicopter and air-taxi operations before urban airspace bottlenecks emerge.
|
Region |
Key Characteristics | Primary Growth Driver |
| North America | Mature market, high regulatory standards (FAA), advanced HEMS network, shale activity. |
Offshore Wind (East Coast), HEMS, Law Enforcement. |
|
Europe |
High regulatory pressure (EASA), leading in offshore wind (North Sea), dense HEMS network. | Offshore Wind, Search & Rescue (SAR), VIP Transport. |
| Asia-Pacific | Highly fragmented, rapid growth, varying regulatory maturity, vast offshore potential. |
Oil & Gas (Southeast Asia), Offshore Wind, Utility. |
|
Latin America |
Dominated by offshore Oil & Gas (Brazil), untapped potential in mining and VIP transport. | Oil & Gas, Mining Support. |
| Middle East | High concentration of VIP and executive transport, expanding offshore operations. |
VIP Transport, Oil & Gas, Tourism. |
Key Market Drivers: A Multi-Faceted Growth Engine
Growth is no longer monolithic. It is being driven by a confluence of factors across different verticals.
Resurgence in Oil & Gas Exploration
-
-
- While the energy transition is underway, global demand for oil and natural gas will remain robust in the near-to-medium term. New offshore projects in regions like the Gulf of Mexico, Brazil, and West Africa are driving demand for crew change, transport, and surveillance services. However, this segment’s growth is tempered by volatility and a long-term strategic need for diversification.
-
The Unstoppable Rise of Offshore Wind
-
-
- This is the single most significant growth vector. Governments worldwide, particularly in Europe, North America, and Asia, are aggressively pursuing offshore wind targets. Global offshore wind capacity is set to increase 15-foldover the next two decades. Helicopters are indispensable for the construction and maintenance of these far-offshore installations, offering faster transit times and the ability to operate in higher sea states than crew transfer vessels.
- While ROI headwinds, including 2024 U.S. cancellations (9.7 GW) and 50% LCOE inflation, have slowed near-term momentum, policy resilience via EU Net-Zero Industry Act, IRA credits, and Asia’s floating wind push ensures sustained demand.
-
The Criticality of Emergency Medical Services (HEMS)
-
-
- HEMS has evolved from a niche service to a cornerstone of modern emergency response networks. Data highlights a consistent annual increase in HEMS flights, driven by an aging population, the need for rapid trauma care, and the expansion of coverage to rural areas. This segment provides a stable, counter-cyclical revenue stream for operators.
-
Urban Air Mobility (UAM) and Advanced Air Mobility (AAM)
-
-
- While still in its nascent stages, the development of electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft represents both a disruption and an opportunity. The role of traditional helicopter operators in shaping this ecosystem through infrastructure development, operational expertise, and regulatory compliance cannot be overstated.
-
The Strategic Challenge: Operational Excellence in a High-Stakes Environment
Success in this market is contingent upon mastering three core challenges:
-
-
- The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Imperative: With legacy fleets aging, maintenance, fuel, and insurance costs constitute a significant portion of operational expenditure. The most successful operators are those implementing predictive maintenance analytics, powered by AI and IoT sensors, to minimize unscheduled downtime and extend component lifecycles. This is a direct lever on profitability.
- The Sustainability Mandate: Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are now central to investment and contracting decisions. Regulatory pressure, such as the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA)‘s decarbonization roadmap, is mounting. The adoption of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), investment in quieter and more fuel-efficient rotorcraft (like the Airbus H160), and the long-term roadmap towards hybrid-electric propulsion are no longer speculative but essential for future-proofing operations.
- The Human Capital Equation: The global pilot and technician shortage remains a critical bottleneck. Attracting and retaining talent requires innovative training programs, competitive compensation, and a clear commitment to safety and technology.
-
Strategic Recommendations for Market Participants
To capitalize on the evolving landscape:
-
-
- Diversify Service Portfolios: Reduce over-reliance on any single sector, particularly Oil & Gas. Actively pursue contracts in offshore wind, HEMS, and utility services (power line inspection, etc.).
- Embrace the Digital Fleet: Invest in fleet management software, health and usage monitoring systems (HUMS), and data analytics to drive down TCO and enhance safety metrics.
- Formulate a Proactive ESG Strategy: Develop a clear roadmap for SAF integration, noise reduction, and carbon emission tracking. This is increasingly a prerequisite for winning major contracts.
- Forge Strategic Alliances: Partner with eVTOL developers, technology firms, and infrastructure providers to secure a role in the emerging AAM ecosystem.
- Invest in the Talent Pipeline: Develop apprenticeship and ab-initio training programs to secure a future pipeline of pilots and technicians.
-
Conclusion
The global helicopter services market is at a strategic crossroads. The trajectory is one of growth, but it is a growth that is increasingly segmented, technologically driven, and constrained by cost and sustainability pressures. The era of competing solely on asset ownership is over. The future belongs to data-driven, strategically diversified, and environmentally conscious operators who can demonstrate superior value and operational resilience. For those willing to adapt, the opportunities for profitable and sustainable growth are significant.
Partner with us to future-proof your operations against market shifts and disruptors.



