The Strategic Context: Beyond Refrigeration, Towards Resilience
In today’s volatile global economy, cold chain logistics is no longer merely operational, it’s a strategic imperative. Leveraging stable, integrity-driven cold chains reduce food loss, enables equitable vaccine access, and unlocks sustainable growth.
Key Imperatives:
-
-
- Address systemic gaps causing over 500 million tons of global food loss, equivalent to 12 % of global production, due to insufficient refrigeration.
- Vaccine wastage due to cold chain failures likely ranges from 10 to 30% globally, with an average of 20 to 25% when including both routine and mRNA vaccines.
- Future proof energy consumption: agrifood systems consume ~ 30% of global energy post-farmgate, with 70 % in logistics, processing, and storage.
-
Strategic Stakes:
-
-
- Closing cold-chain gaps can save 144 million tons of food annually in developing economies.
- Public health breakthroughs (e.g., mRNA vaccines) demand ultra-cold logistics. Drones delivering cold-chain payloads in Ghana, Kenya, and Rwanda are pioneering tactical extensions.
- Leading cold storage firms (like Lineage) validate scale. Lineage’s IPO valued their U.S. warehouse footprint at over USD 18 billion.
-
Executives should focus on lane integrity, energy-smart design, and modular expansion to turn cold chain from cost center into a competitive moat.
Market Breakdown & Opportunity Pools
Food Cold Chain:
-
-
- Inefficient cold chain infrastructure costs the global economy an estimated nearly $950 billion per year.
- Developing countries refrigerate only ~20% of perishables versus ~60% in advanced economies – creating opportunity for catch-up.
- Successful pilot: India’s kinnow export cold chain reduced losses by 76%, improved farm income by 23%, and cut emissions 16%.
-
Vaccine & Medical Cold Chain:
-
-
- India’s eVIN platform monitors 27,000 cold-chain points and logs 2 million+ transactions, delivering multi-fold ROI on investment.
- Gavi and Kenyan government’s hub with DHL provides comprehensive supply visibility, reducing waste and inefficiency.
-
Energy & Infrastructure Context:
-
-
- Rwanda’s ACES is building capacity in sustainable cooling and training technicians for scalable deployment.
-
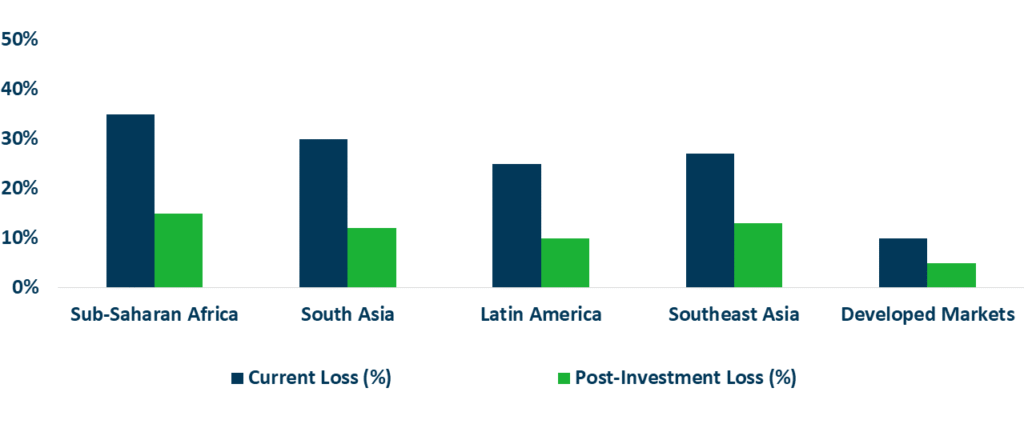
Impact of Cold Chain Investment on Reducing Food Loss
The Operational Realities: Confronting the Implementation Hurdles
Strategy falters without execution. These are the operational realities we consistently navigate with clients:
-
-
- The True Cost of Failure is Hidden: The direct loss from spoiled goods is merely the initial cost. The compounded impact includes regulatory fines, contract penalties, lost market share, and irreparable damage to brand equity that took decades to build.
- Strategic Infrastructure: A facility handling frozen goods is not equipped for +2°C to +8°C biologics. The partner ecosystem is fragmented. Your selection criteria for 3PLs must be ruthlessly aligned with your specific product portfolio and risk tolerance.
- Sustainability is an Operational and Financial Mandate: The environmental footprint of cold chains is under intense scrutiny from investors, regulators, and consumers. The transition to natural refrigerants (like CO2) and fleet electrification is no longer a “green” initiative but a calculated decision for long-term operational efficiency and cost containment.
-
Strategic Pillars & Execution Levers
|
Pillar |
Hypothesis | Action |
KPI (Target) |
|
Pillar A – Digital Visibility for Integrity |
High-value cargo fails due to poor monitoring. | Launch mobile-enabled monitoring (akin to eVIN) across top-tier lanes. | Vaccine wastage reduction target 50%. |
| Pillar B – Modular Energy-Smart Nodes | Energy costs inhibit expansion. | Deploy solar-powered, containerized cold hubs; use Kigali/ACES for design. |
kWh per kg of storage – target 30% cut. |
|
Pillar C – Value-Added Cold Services |
Margin frozen in capacity. | Add repacking, pre-cool, GDP documentation at hubs. | Margin per pallet – lift by 10 to 15%. |
| Pillar D – Resilient Last-Mile Solutions | Traditional logistics fail rural reach. | Deploy drones or solar-backed cold-box networks for remote last mile. |
Delivery success rate >95%. |
|
Pillar E – Public-Private Partnerships |
Governments lack private efficiency. | Structure PPPs to fund cold hubs in agri clusters. |
Farmer income increases 20%; food loss drop 50%. |
Strategic Recommendations
To position your organization for success in the cold chain logistics market, consider the following:
1. Commission a Zero-Based Cold Chain Design
Do not audit your current network. Start from a blank page. Map the precise temperature, time, and visibility requirements of every product SKU against your existing assets and partner capabilities. This exercise will reveal critical vulnerabilities and wasteful redundancies.
2. Mandate Interoperable Data as a Contractual Prerequisite
Any partner in your ecosystem from origin cold storage to last-mile carrier must provide seamless, API-fed data integration into your central control tower. Make this a non-negotiable condition in all new contracts and RFPs.
3. Define Your “Biologics Readiness” Strategy
This is a definitive strategic choice. Will you build (CAPEX intensive), buy (M&A), or partner (strategic JV) to capture this high-margin market? A clear decision is required in this fiscal year to avoid being sidelined.
4. Appoint a Single Point of Accountability
Diffused responsibility is the primary reason for cold chain failure. appoint a dedicated, C-suite empowered leader (e.g., a VP of Cold Chain Excellence) with the authority to break silos between Procurement, Logistics, Quality, and IT.
Conclusion: The Strategic Inflection Point
The evolution of the global cold chain logistics is at a strategic inflection point. It is no longer a niche logistical consideration but a central pillar of modern commerce and healthcare. The convergence of pharmaceutical innovation, consumer demand for fresh global perishables, and the relentless rise of e-commerce has thrust this once-backroom operation into the C-suite spotlight.
Organizations that continue to treat it as a generic transportation cost will find themselves outpaced by more agile, intelligent, and resilient competitors. The volatility of global supply chains has made one truth abundantly clear: vulnerability in the cold chain is a direct threat to revenue, brand reputation, and market share.
Success will be determined by the ability to harness data for predictive insights, forge partnerships based on transparency and performance, and embed sustainability into the core of cold chain operations. This requires a fundamental shift in mindset, investment, and organizational structure. The winners in the next decade will be those who execute on the following imperatives:
-
-
- Elevate Cold Chain Governance: Appoint a single, empowered leader with end-to-end accountability.
- Prioritize Data Interoperability: Mandate seamless data integration from all partners as a non-negotiable contract term.
- Invest in Predictive Intelligence: Shift resources from simple monitoring to AI-driven predictive asset management.
- Solve the Last-Mile Brand Experience: Develop a proprietary or exclusive last-mile solution that guarantees product integrity and elevates customer trust.
-
Let’s begin your strategic diagnostic. Schedule a briefing with our specialists to pressure-test your cold chain resilience.



