In an era of accelerating climate imperatives and volatile energy markets, corporations are increasingly turning to Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) as a cornerstone of their sustainability strategies. Corporate PPAs involve long-term contracts where businesses directly procure renewable energy from generators, bypassing traditional utility intermediaries. This mechanism not only secures predictable energy costs but also enables firms to meet ambitious decarbonization targets, such as those aligned with the Paris Agreement and net-zero commitments.
From a global perspective, the corporate PPA market represents a pivotal shift toward market-driven renewable deployment, fostering innovation in energy procurement while addressing regulatory and economic pressures. In 2023 corporates contracted a record level of wind and solar PPAs (46 GW), underlining rapid market maturation and growing geographic breadth.
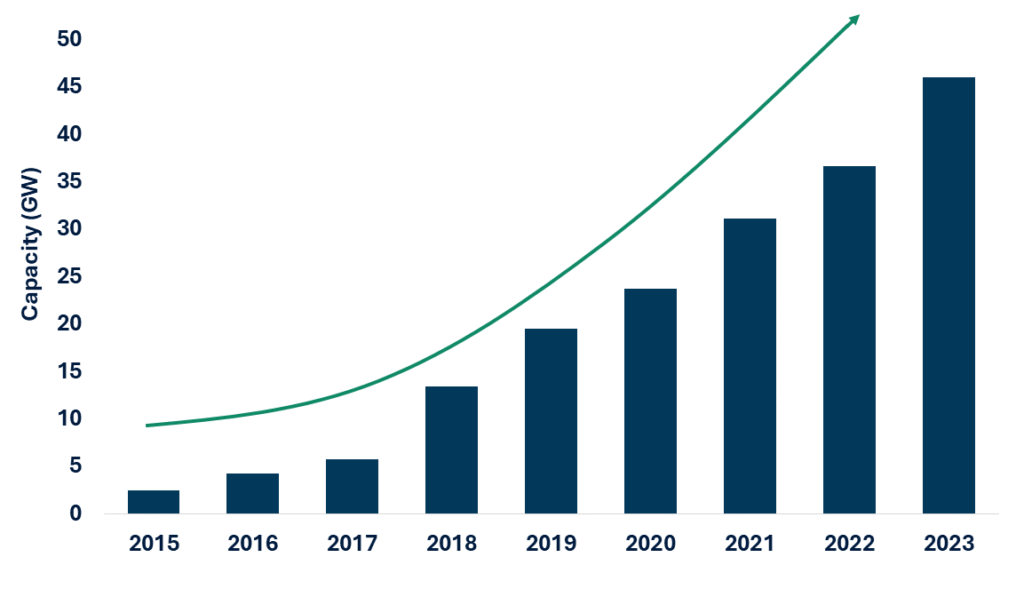
Global Annual Corporate PPA Volumes (2015-2023)
The Corporate PPA Defined: A Strategic Financial and Energy Instrument
A Corporate PPA is a long-term contract between an energy buyer (a corporation) and a developer/operator of a renewable energy asset (typically solar or wind). Under this agreement, the corporation agrees to purchase electricity, its associated energy attributes (Renewable Energy Certificates or Guarantees of Origin), and sometimes balancing services for a predetermined price and duration.
The value proposition of a PPA has three core strategic pillars:
1. Financial Hedging
PPAs lock in energy costs for 10-15 years, insulating corporate operations from volatile wholesale electricity prices. In an era of unprecedented price volatility, this provides exceptional budget certainty.
2. Decarbonization & ESG Credibility
PPAs are the most credible and scalable mechanism for corporations to substantiate Scope 2 emission reduction claims under the GHG Protocol. They directly enable the addition of new renewable capacity to the grid, a claim known as “additionality”, which is increasingly demanded by investors, regulators, and consumers.
3. Brand Differentiation & Competitive Positioning
A well-executed PPA strategy signals market leadership, enhances brand value, and helps attract and retain top talent who prioritize working for environmentally responsible organizations.
Global and Regional Volumes
From a global vantage, corporate PPA volumes have diversified across regions, with North America and Europe historically dominant but Asia-Pacific emerging rapidly.
North America: The U.S. remains the world’s most mature PPA market, driven by a favorable regulatory environment, liquid financial markets, and strong corporate demand. The Inflation Reduction Act has further accelerated project economics, solidifying the VPPA as the structure of choice for sophisticated offtakers.
Europe: The European market is characterized by its diversity. Countries like Spain, the UK, and the Nordics are highly active, driven by ambitious EU-wide decarbonization targets and high wholesale power prices. Navigating the complex patchwork of national laws and Guarantee of Origin systems is a primary challenge and requires localized expertise.
Asia-Pacific: While emerging, the APAC region holds immense potential. Australia leads with a mature market, while countries like Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan are developing supportive policies. The primary challenge is often the immaturity of the grid infrastructure and regulatory uncertainty, making de-risking strategies paramount.
|
Region |
Estimated PPA-Driven Capacity Addition (GW, 2024-2030) | Key Statistics and Trends |
| United States | ~500 |
Tax incentives boost utility-corporate deals; data centers drive 40% of demand. |
|
European Union |
~300-400 | Doubling of prior achievements; 157 first-time signers in 2024. |
| Asia-Pacific | ~200-250 |
9.7 GW in 2023; rapid growth in Korea (30 GW forecast). |
|
Latin America & Caribbean |
~100-150 | Bilateral PPAs in Brazil and Mexico; 46-79% market-driven growth. |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | ~50-80 |
Liberalization in South Africa, Kenya; >30% accelerated growth potential. |
|
Middle East & North Africa |
~40-60 |
Emerging industrial decarbonization; policy reforms enabling bilateral agreements. |
Key Risks and Mitigation Strategies
Entering a PPA without a robust risk mitigation framework can transform a strategic advantage into a financial liability.
-
-
- Volume & Price Risk (Cannibalization): In a VPPA, the offtaker is exposed to the difference between the contract price and the wholesale market price. A prolonged period of low market prices can lead to significant financial settlements. Mitigation: Detailed fundamental price forecasting, structuring with collars or floors, and portfolio diversification.
- Counterparty & Credit Risk: The failure of either the developer or the corporation can jeopardize the project. Mitigation: Rigorous due diligence on the developer’s financials and track record, and the use of corporate guarantees or letters of credit.
- Regulatory & Policy Risk: Changes in government incentives or energy policy can alter project economics. Mitigation: A deep understanding of the local political landscape and structuring agreements with specific change-in-law clauses.
- Execution & Operational Risk: Delays in project construction or underperformance of the asset. Mitigation: Robust technical due diligence, performance guarantees, and liquidated damages for delays.
-
The Path Forward: Integrating PPAs into Corporate Strategy
For C-suite leaders, the question is no longer if to engage with PPAs, but how. A successful PPA strategy must be integrated, not siloed. It requires collaboration between the CFO’s office (financial risk), the COO’s office (energy procurement), and the CSO’s office (sustainability targets).
We advise our clients to begin with a structured internal assessment:
-
-
- Load & Goals Analysis: Quantify your global electricity consumption and define clear decarbonization targets.
- Risk Appetite: Determine the corporation’s tolerance for financial and volumetric risk to select the appropriate PPA structure (physical vs. virtual).
- Geographic Prioritization: Identify regions with favorable market conditions, aligned with your operational footprint and risk profile.
- Execution Readiness: Secure internal stakeholder alignment and prepare the necessary legal and financial resources to move swiftly in a competitive market.
-
Conclusion
The global Corporate PPA market represents a fundamental shift in how companies secure energy, manage costs, and execute on their climate commitments. The data confirms its trajectory from a marginal activity to a mainstream corporate strategy. The complexity and dynamism of this landscape, however, demand a sophisticated, well-informed approach.
Corporations that proactively develop an integrated PPA strategy, backed by deep market intelligence and a clear understanding of risks, will not only future-proof their operations but will also secure a decisive competitive edge in the low-carbon economy.
Contact our Energy Strategy Practice to architect a bespoke PPA strategy that de-risks your energy portfolio and accelerates your decarbonization goals.



