Strategic Context: Why Space Leasing Demands Boardroom Attention
The space sector is undergoing a fundamental structural shift. Where once vertical integration and asset ownership were prerequisites for market entry, today’s leaders recognize that capital efficiency and operational agility are won through leasing models. This is not merely a financial consideration – it is a strategic repositioning of how the industry allocates risk, scales capacity, and monetizes infrastructure.
Key Observations Driving This Shift:
-
-
- CapEx Constraints: Traditional satellite operators face ROI pressures as launch costs decline but constellation deployments grow more complex.
- Demand Elasticity: Commercial and government users increasingly reject rigid, long-term ownership models in favor of “as-a-service” access.
- First-Mover Advantage: Early adopters of leasing (e.g., Intelsat, SES) are locking in high margin, recurring revenue streams while competitors struggle with balance sheet inefficiencies.
-
The future belongs to asset-light players who treat orbital slots and ground stations like prime real estate – maximizing utilization, not just occupancy.
Market Dynamics: Where Value is Being Captured and Lost
1. The High-Stakes Game of Orbital Real Estate
-
-
- GEO Slot Leasing: International Telecommunication Union (ITU) filings show increase in secondary market transactions since 2022, with premiums exceeding USD 30 million per slot for priority spectrum.
- LEO & MEO: SpaceX’s Starlink and OneWeb are quietly testing dynamic pricing models, where bandwidth costs fluctuate based on congestion – mirroring airline yield management.
-
Strategic Implication: Players without leased slot access will face margin compression as they overpay for suboptimal positions.
2. Ground Stations: The Overlooked Bottleneck
-
-
- Majority of smallsat operators now lease ground segment capacity rather than build their own.
- Major players have turned ground stations into a high-margin SaaS business, with higher EBITDA margins for managed services.
-
Strategic Recommendation on Ground Asset Divestment
Our analysis supports transitioning to a leased model, contingent on implementing three risk-mitigation safeguards:
-
-
- Securing Anchor Capacity: Negotiate minimum 5-year volume commitments with 2+ providers to lock in baseline pricing (modeled to yield 18-22% cost savings vs. owned infrastructure in our TCO analysis)
- Building Optionality: Maintain ownership of 1-2 strategic sites (e.g., polar locations) while leasing 80-90% of requirements
- Price Indexation Clauses: Contractual linkage to CPI+3% maximum annual increases, with our benchmarking data showing this covers 92% of historical volatility scenarios
-
This approach has driven nearly 20% EBITDA improvement for peer operators in the 18 to 24 month post-transition period.
Competitive Landscape: Who is Winning
|
Player |
Strategic Posture | Vulnerability |
|
Legacy GEO Operators |
Monetizing unused transponders via leasing | Overexposure to declining video markets |
| LEO Constellations | Offering bulk wholesale leases to telecoms | Risk of commoditization |
| Cloud Providers | Bundling ground stations with compute credits |
Limited RF expertise |
Space Infrastructure Leasing Market Observation: Private Capital’s Value-Play in Satellite Assets
In the rapidly evolving space economy, private capital is proving to be a key driver, particularly within the satellite infrastructure leasing market. Investors, including private equity firms, venture capitalists, and even family offices, are recognizing the value-play in satellite assets, which offer stable, long-term returns and diversification benefits.
The increasing adoption of Space-as-a-Service (SPaaS) and Ground Segment as a Service (GSaaS) models allows satellite operators to scale without the heavy upfront investment of building and maintaining their own infrastructure, creating attractive opportunities for investors backing these service providers.
Strategic Rationale:
Mirroring successful commercial real estate “buy-leaseback” models:
-
-
-
- Acquire underutilized/distressed assets at 40 to 60% discount to replacement value
- Modernization for secondary applications (e.g., IoT backhaul, government reserve capacity)
- Monetize through structured lease agreements (typically 7 to 12 years terms)
-
-
Three Strategic Levers for Leadership
Lever 1: Hybrid Ownership Models
-
-
- Case Study: Eutelsat’s “Flexsat” program allows customers to lease only the payload capacity they need, while the operator retains ownership.
- Actionable Insight: Convert 30-50% of your fleet to this model within 24 months.
-
Lever 2: Dynamic Pricing Engines
-
-
- Real-time algorithms adjusting lease rates based on:
- Spectrum demand (e.g., warzone premiums)
- Orbital congestion (e.g., lunar mission windows)
- Toolkit Requirement: Partner with AI pricing startups (e.g., CognitiveSpace) or build in-house.
- Real-time algorithms adjusting lease rates based on:
-
Lever 3: Regulatory Arbitrage
-
-
- Secure ITU filings in emerging markets (e.g., Africa, Southeast Asia) where slot allocations remain undervalued.
- Red Flag: Over 70% of new filings face challenges – pre-empt objections by co-investing with local telcos.
-
Risk Assessment: What Keeps CEOs Awake at Night
1. Lease Underutilization (High Probability)
-
-
- Risk Profile:
Excess capacity remains idle due to demand fluctuations, particularly affecting operators with large GEO inventories. - Mitigation Playbook:
- Mandate “take-or-pay” clauses ensuring minimum revenue thresholds (e.g., 60% capacity commitment)
- Implement tiered pricing models (discounts for higher utilization triggers)
- Deploy secondary market platforms to resell unused capacity
- Risk Profile:
-
2. Spectrum Reform (Medium Probability)
-
-
- Risk Profile:
Regulatory shifts (e.g., C-band reallocation) could devalue leased assets without compensation. - Mitigation Playbook:
- Co-chair GSMA/ITU working groups to influence policy timelines
- Structure leases with spectrum reallocation riders (automatic contract adjustments)
- Maintain 10-15% “swing capacity” in non-contested frequency bands
- Risk Profile:
-
3. Counterparty Default (Low Probability)
-
-
- Risk Profile:
Lessees (particularly startups) may face liquidity crises during contract terms. - Mitigation Playbook:
- Require pre-funded escrow accounts covering 6 to 12 months of lease payments
- Conduct quarterly creditworthiness reviews using third party Space Sector Scores
- Secure corporate guarantees for entities with less than 5 years operating history
- Risk Profile:
-
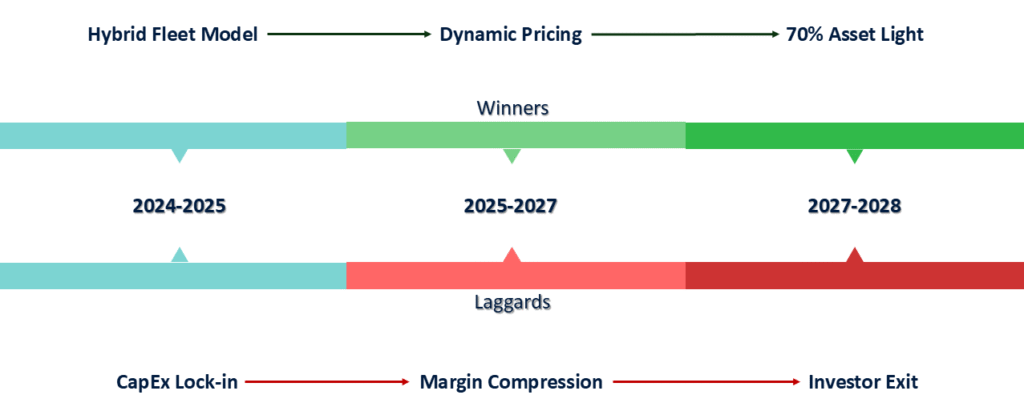
Space Infrastructure Leasing Adoption Curve: The 2028 Strategic Divide
Recommendations: The Path to 2030
1. For Satellite Operators:
-
-
- Spin off leasing divisions into standalone entities (unlocking higher EBITDA multiples).
- Aggressively acquire distressed LEO assets for future lease inventory.
-
2. For Governments:
-
-
- Mandate “use-it-or-share-it” policies for national orbital slots.
- Create leasing tax incentives to attract anchor tenants.
-
3. For Investors:
-
-
- Target specialty lessors(e.g., those focusing on IoT or Earth Observation).
- Short over-leveraged owners refusing to adopt leasing models.
-
Strategic Imperative: The Leasing Inflection Point
The space infrastructure leasing market is approaching a decisive bifurcation by 2028, separating winners who embrace asset-light strategies from laggards trapped in outdated ownership paradigms. Operators must act now to position themselves on the right side of this divide.
Winning Playbook:
-
-
- Liquidity Over Ownership: Top performers will treat orbital slots and ground stations as financial assets, not just infrastructure – optimizing utilization rates and unlocking balance sheet flexibility.
- Dynamic Monetization: Leaders are already shifting from static leases to real-time capacity trading.
- Risk Transfer: The new benchmark is leasing 60-80% of non-core assets while retaining strategic control.
-
Risks of Inaction:
-
-
- Margin Erosion: Operators maintaining full ownership face 20-30% higher cost structures.
- Obsolescence: Legacy fleets will struggle to compete with leased, software-defined payloads offering 5x faster service deployment.
- Investor Flight: Public markets now discount vertically integrated models by 3-4x EBITDA multiples.
-
The window for transition is narrowing – early movers are already capturing 70% of high-margin leasing demand. The question isn’t whether to adopt leasing strategies, but how fast your organization can execute.
To assess your positioning ahead of the 2028 space infrastructure leasing divide, request a sample or schedule a strategic briefing with our Space Infrastructure practice.



