Introduction
The aviation industry operates in a high-stakes environment where risk management is not just a regulatory requirement – it’s a business imperative. With global air traffic rebounding and surpassing post-pandemic levels, aviation insurers and aviation stakeholders face evolving challenges:
-
-
- Rising claim severity due to inflation-driven aircraft parts costs (Over 30% increase since 2020)
- Geopolitical risks (Russia-Ukraine war, and Middle East tensions disrupting coverage terms)
- Climate change impacts (increased turbulence claims, over 50% increase since 2000)
-
Hence, the aviation insurance market is undergoing unprecedented disruption. With premiums increasing over 150% since 2020 and catastrophic claims severity up 165%, traditional risk transfer mechanisms are failing to keep pace.
The Shifting Aviation Insurance Landscape: Key Trends
1. Hard Market Conditions Persist
-
-
- Premiums up 20-30% YoY due to:
- Loss creep from past claims (e.g., engine recalls costing over USD 3 Billion in claims)
- Reinsurance tightening (A major reinsurer reduced aviation exposure by 15% in 2023)
- Premiums up 20-30% YoY due to:
-
2. War Risk Exclusions & Geopolitical Challenges
-
-
- Russian aircraft seizures led to over USD 10 Billion in contested claims.
- Israel-Iran tensions triggered 30% premium spikes for Middle East overflights.
-
Strategic Takeaway:
-
-
- Long-term contracts (3+ years) can lock in rates before further hikes.
- Captive insurance models are gaining traction among large operators (e.g., Delta’s captive insures USD 1.2 Billion in hull coverage).
- Dual-flag registrations (e.g., Ireland/Bermuda) improve war risk flexibility.
- Alternative risk transfer (parametric insurance) for predictable payouts during airspace closures.
-
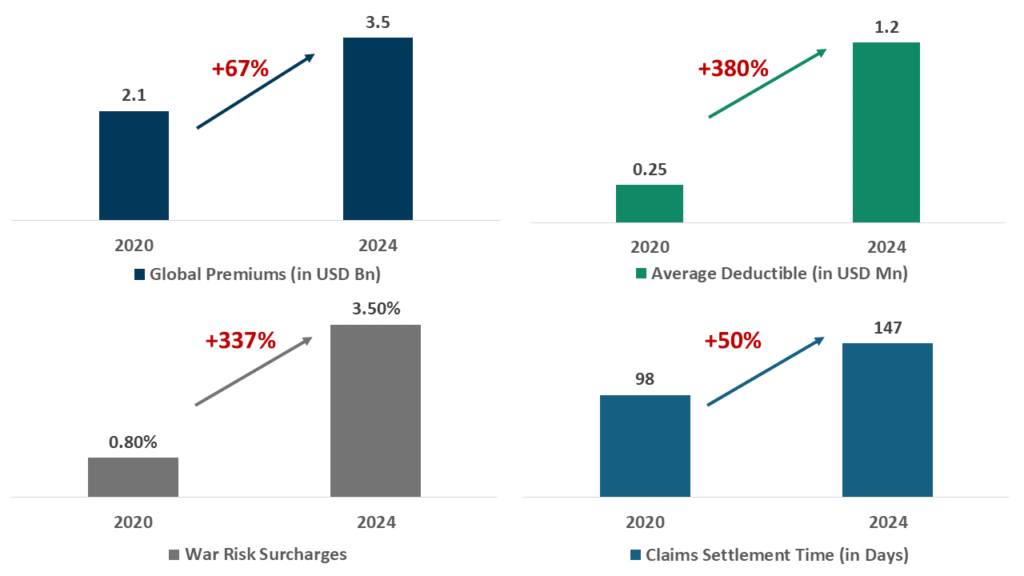
Aviation Insurance Market Statistics – 2020 vs 2024
Cost Drivers in Aviation Insurance (And How to Control Them)
1. Claims Inflation: The Hidden Threat
-
-
- Aircraft part costs up 35% (Nose gear now cost USD 1.8 million vs. USD 1.3 million in 2020).
- Labor shortages (Over 15% gap in A&P mechanics) delay repairs, increasing downtime claims.
-
2. Fleet Age & Technology Risks
-
-
- Older fleets (20+ years) pay 40% higher premiums.
- Cyber risks (200% increase in avionics hacking attempts since 2021).
-
Mitigation Strategies:
-
-
- Pre-negotiate labor rates with MROs in insurance contracts.
- 3D printing adoption for non-critical parts (saves 15-20% on AOG claims).
- Retrofit investments (Upgrades can cut premiums by 8 to 12%).
- Silent cyber endorsements to close coverage gaps.
- Claims Collaboration Clauses: Pre-negotiated adjuster teams cut settlement time by 40%
-
By strategically layering deductibles – particularly for high-exposure risks exceeding USD 5 million – organizations can achieve an average premium reduction of 22%. This approach shifts retained risk to manageable tiers while maintaining catastrophic coverage. Insurers reward this structured risk assumption with improved pricing, though it requires robust cash flow planning to cover the stacked deductibles.
Implementing sub-limits on non-core exposures (e.g., catering liability) yields 9 – 15% premium savings. This technique focuses coverage on high-severity risks while capping attritional losses.
Emerging Risks Requiring Proactive Management
1. Climate Change & Turbulence Claims
-
-
- Clear-air turbulence has increased by over 50% since 2000.
- 2023 saw USD 500 Million in turbulence injury claims.
-
2. Lithium Battery Fire Risks
-
-
- EVTOL & cargo operators face 300% higher fire liability premiums.
- FAA recorded 350+ battery thermal events in 2023.
-
Strategic Takeaway:
-
-
- Real-time weather analytics integration (e.g., WSI Fusion) reduces exposure.
- Crew training upgrades (Lufthansa’s program cut turbulence injuries).
- AI-powered cargo scanners (X-ray AI detects faulty batteries at 95% accuracy).
- Dedicated battery fire containment systems (reduces hull loss risk by 50%).
-
Strategic Recommendations for 2024-2025
1. For Airlines & Lessors
-
-
- Diversify insurer panels (avoid over-reliance on major players, which holds over 55% market share).
- Embedded insurance (passenger-paid coverage boosts revenue USD 2 to 5 per ticket).
-
2. For MROs & FBOs
-
-
- Negotiate “repair cost caps” in liability policies.
- Demand “waiver of subrogation” clauses to avoid insurer lawsuits post-claim.
-
3. For Insurers
-
-
- Leverage telematics (QAR/FDR data cuts claims processing time by 30%).
- Parametric products for rapid payouts on delays/cancellations.
-
Conclusion: Transforming Aviation Insurance from Cost Center to Strategic Asset
The aviation insurance market landscape is no longer about passive risk transfer – it’s a strategic lever for competitive differentiation. As premiums harden and exposures multiply, leading operators are redefining their approach by:
-
-
- Embedding predictive analytics to convert claims data into discounted premium (nearly 15-22% savings for early adopters)
- Pioneering alternative risk structures, with over 40% of top-quartile airlines now using captives or parametric triggers
- Rewriting policy language to eliminate silent cyber exclusions and climate-related coverage gaps
-
The new paradigm is clear: Organizations treating insurance as a compliance exercise will hemorrhage cash, while those leveraging it as an operational enabler will gain:
-
-
- 15-25% lower total cost of risk
- 72-hour claims liquidity during crises
- First-mover advantages in emerging markets
-
Ready to benchmark your program against industry leaders?
Get Sample or Schedule a 30-minute Gap Analysis Call with our risk engineering team for your customized requirements.



